Multiple Regression Model:
The statistical technique that use Several explanatory variables to Predict the Outcome of the response variable. The Goal of multiple linear regression (sums billion) is to model the Relationship Between the explanatory and response variables.Multiple linear regression attempts to model the relationship between two or more explanatory variables and a response variable by fitting a linear equation to observed data. Every value of the independent variable x is associated with a value of the dependent variable y. The population regression line for p explanatory variables x1, x2, ... , xp is defined to be
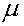 y =
y = 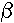 0 +
0 + 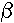 1x1 +
1x1 + 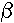 2x2 + ... +
2x2 + ... + 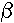 pxp. This line describes how the mean response
pxp. This line describes how the mean response 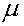 y changes with the explanatory variables. The observed values for y vary about their means
y changes with the explanatory variables. The observed values for y vary about their means 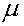 y and are assumed to have the same standard deviation
y and are assumed to have the same standard deviation 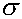 . The fitted values b0, b1, ..., bp estimate the parameters
. The fitted values b0, b1, ..., bp estimate the parameters 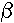 0,
0, 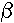 1, ...,
1, ..., 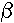 p of the population regression line.
p of the population regression line.Since the observed values for y vary about their means
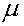 y, the multiple regression model includes a term for this variation. In words, the model is expressed as DATA = FIT + RESIDUAL, where the "FIT" term represents the expression
y, the multiple regression model includes a term for this variation. In words, the model is expressed as DATA = FIT + RESIDUAL, where the "FIT" term represents the expression 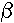 0 +
0 + 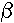 1x1 +
1x1 + 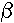 2x2 + ...
2x2 + ... 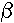 pxp. The "RESIDUAL" term represents the deviations of the observed values y from their means
pxp. The "RESIDUAL" term represents the deviations of the observed values y from their means 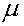 y, which are normally distributed with mean 0 and variance
y, which are normally distributed with mean 0 and variance 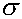 . The notation for the model deviations is
. The notation for the model deviations is 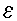 .
.Formally, the model for multiple linear regression, given n observations, is
yi =
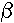 0 +
0 + 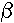 1xi1 +
1xi1 + 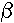 2xi2 + ...
2xi2 + ... 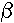 pxip +
pxip + 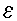 i for i = 1,2, ... n.
i for i = 1,2, ... n.In the least-squares model, the best-fitting line for the observed data is calculated by minimizing the sum of the squares of the vertical deviations from each data point to the line (if a point lies on the fitted line exactly, then its vertical deviation is 0). Because the deviations are first squared, then summed, there are no cancellations between positive and negative values. The least-squares estimates b0, b1, ... bp are usually computed by statistical software.
The values fit by the equation b0 + b1xi1 + ... + bpxip are denoted
The variance
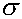 ² may be estimated by s² =
² may be estimated by s² = 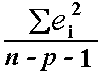 , also known as the mean-squared error (or MSE).
, also known as the mean-squared error (or MSE).The estimate of the standard error s is the square root of the MSE.




